Hip fracture owing to osteoporosis is one of the key public health concerns specially for geriatric people, whose sufferings as well as the cost of treatment can be reduced if the fracture risk can be predicted a priori. Exisitng research focuses on assessing the hip fracture risk from mechanistic viewpoint. In this approach, 2D Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) and/or Quantitative Computed Tomography (QCT) image based 3-dimensional FEA has been conducted to investigate the cumulative effect of anatomical variations in femur and its inhomogeneous material distribution, which varies noticeably between healthy and osteoporotic bone, and the impact load due to fall.
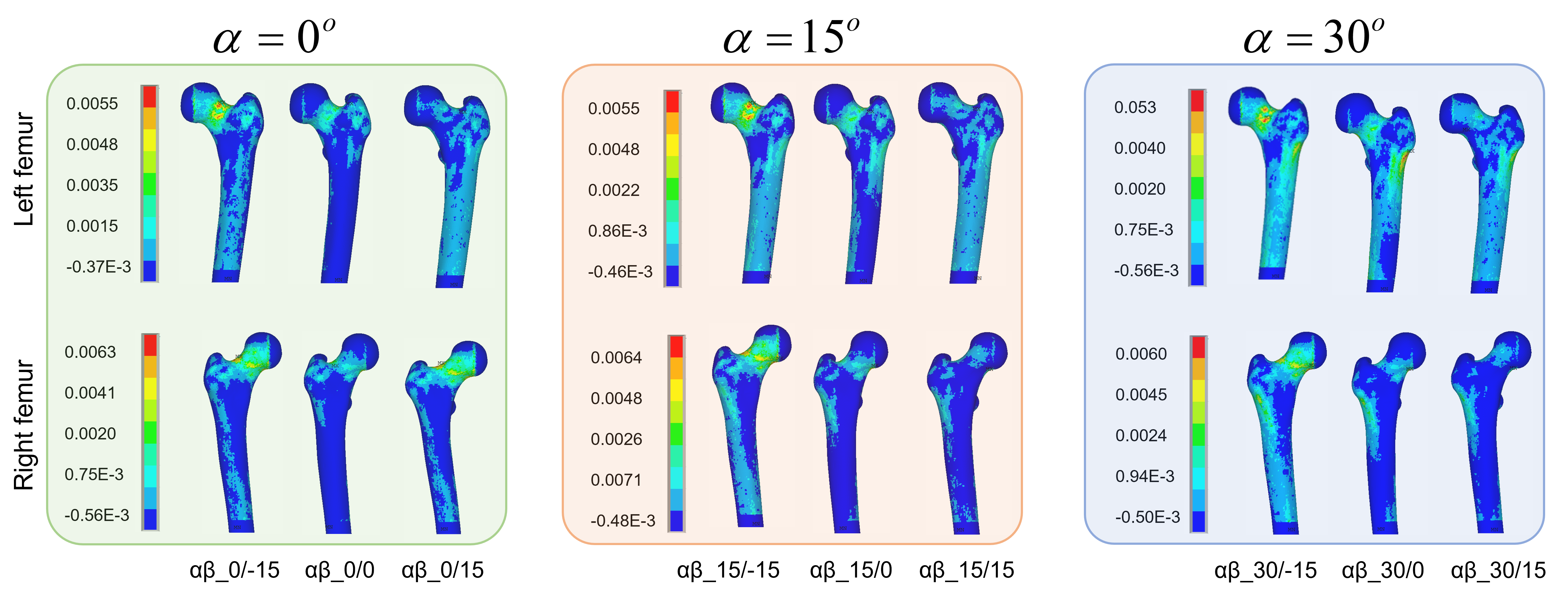
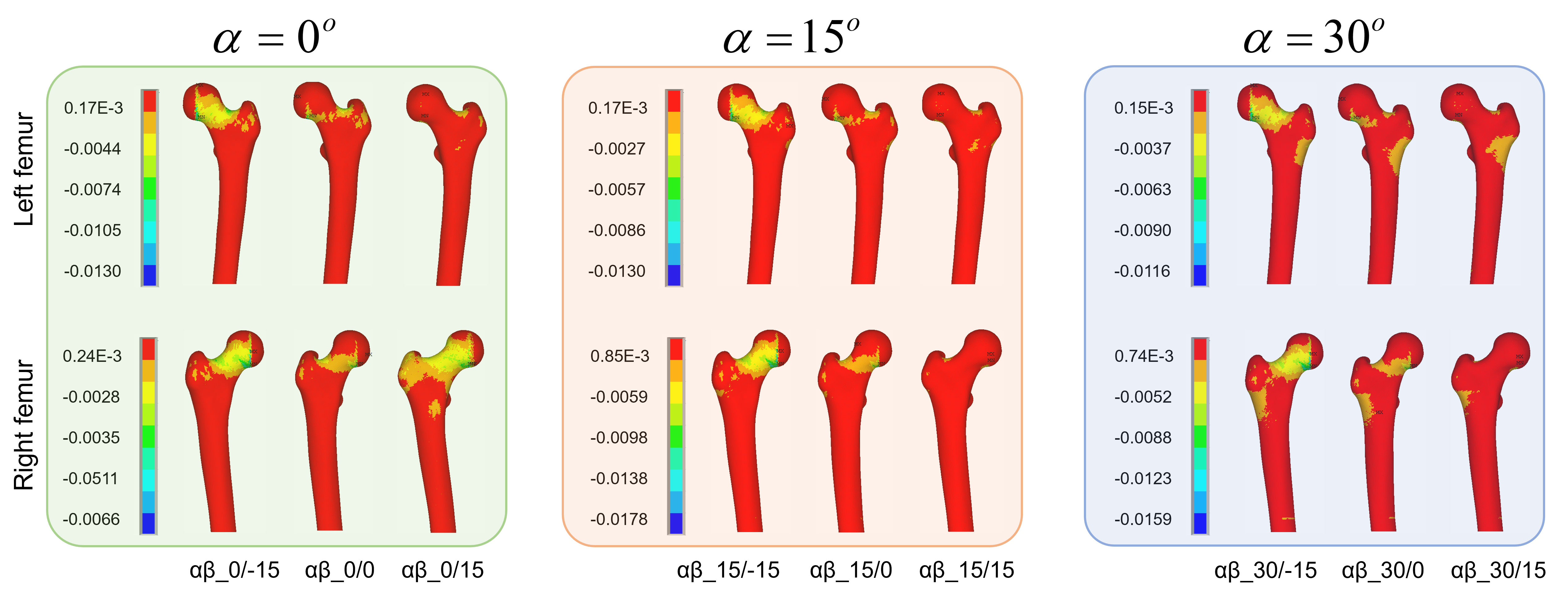
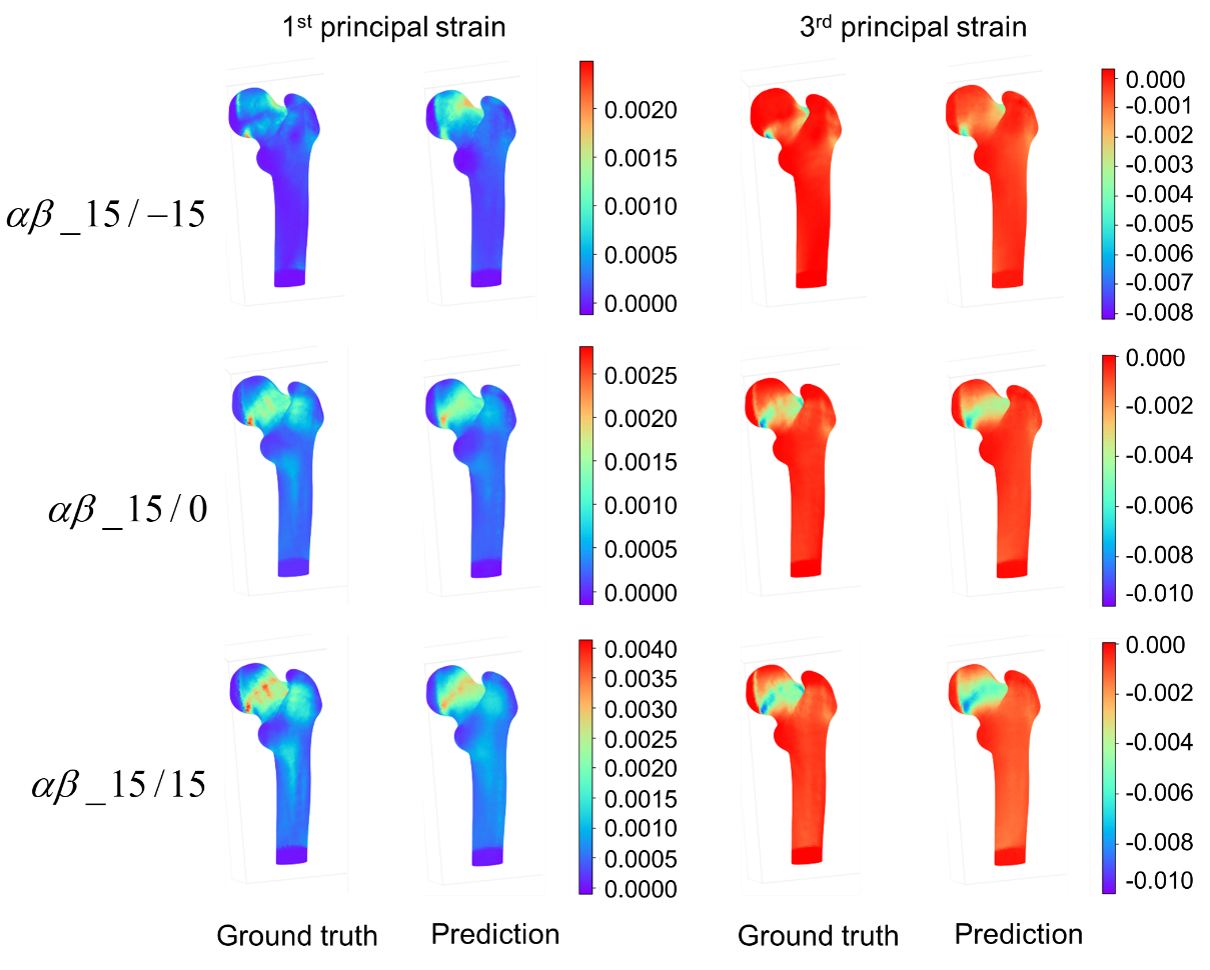
Primarily, a fracture risk indicator based on the ratio of bone stress to strength has been proposed to predict the hip fracture risk. However, conventional computational biomechanical approaches are expensive and require high level of skill set that often limit their clinical application. A data-driven Machine Learning (ML)-based framework can be an alternative but effective approach for disease diagnosis as well as for disease predictions. Therefore, we would like to develop an ML-based modeling approach integrating QCT-based FEA to predict stress-/strain-dependent hip fracture risk, and the visualization of stress/strain by generating surrogate FE models.
J. Sultana, M. Naznin, and T. R. Faisal. SSDL—an automated semi-supervised deep learning approach for patient-specific 3D reconstruction of proximal femur from QCT images, Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing , Springer 62, 1409-1425, 2024. link to PDF
R. Awal and T. R. Faisal. QCT-based 3D finite element modeling to assess patient-specific hip fracture risk and risk factors, Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials Elsevier 150, 106299, 2024. link to PDF
R. Awal and T. R. Faisal. Multiple regression analysis of hip fracture risk assessment via finite element analysis, ASME Journal of Engineering and Science in Medical Diagnostic and Therapy , ASME 4(1), 2021. link to PDF